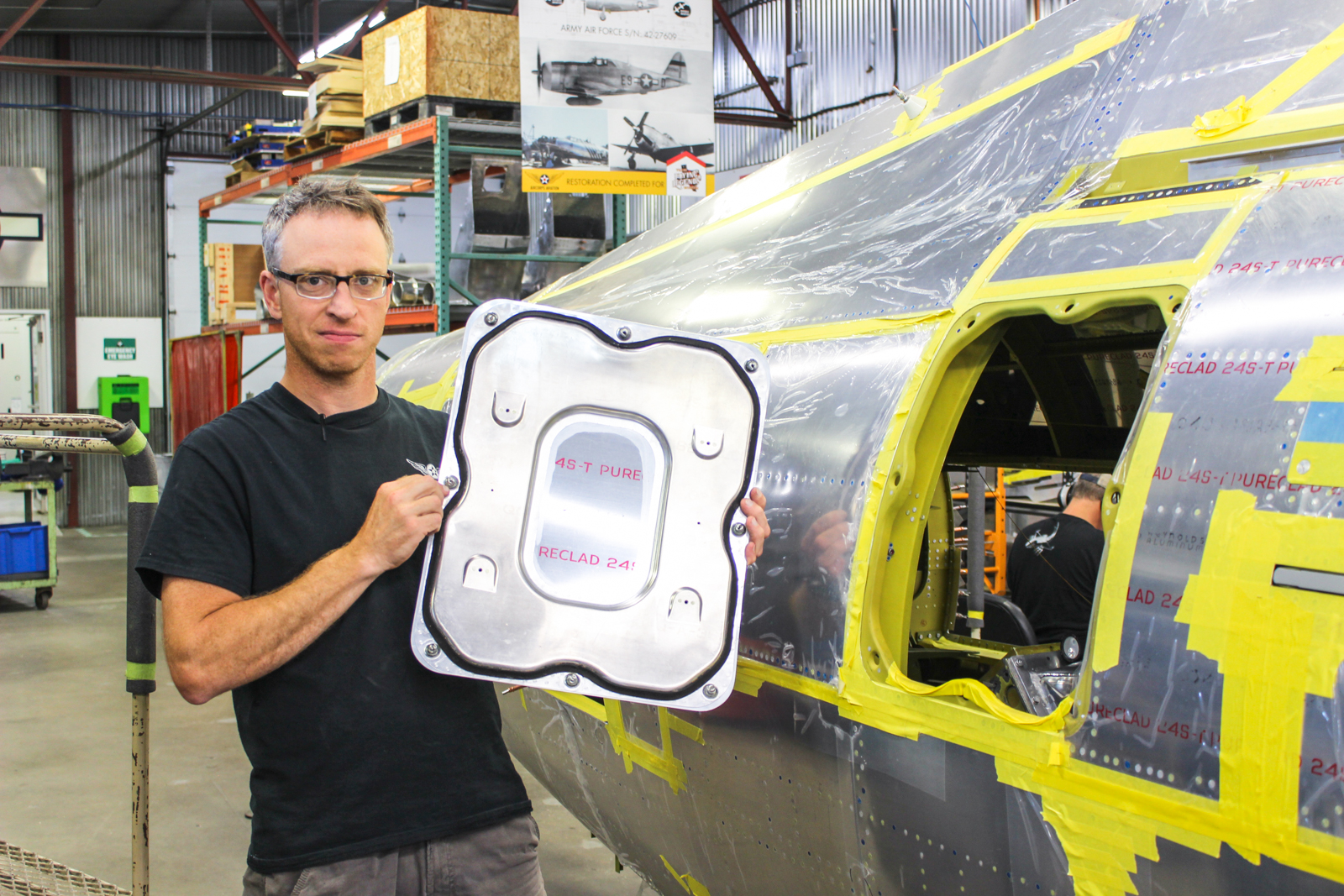
Warbird Digest has just received the August/September, 2019 report from Chuck Cravens concerning the restoration of the Dakota Territory Air Museum’s P-47D Thunderbolt 42-27609 at AirCorps Aviation in Bemidji, Minnesota. We thought our readers would be very interested to see how the project has progressed since our last article on this important project. So without further ado, here it goes!
Update
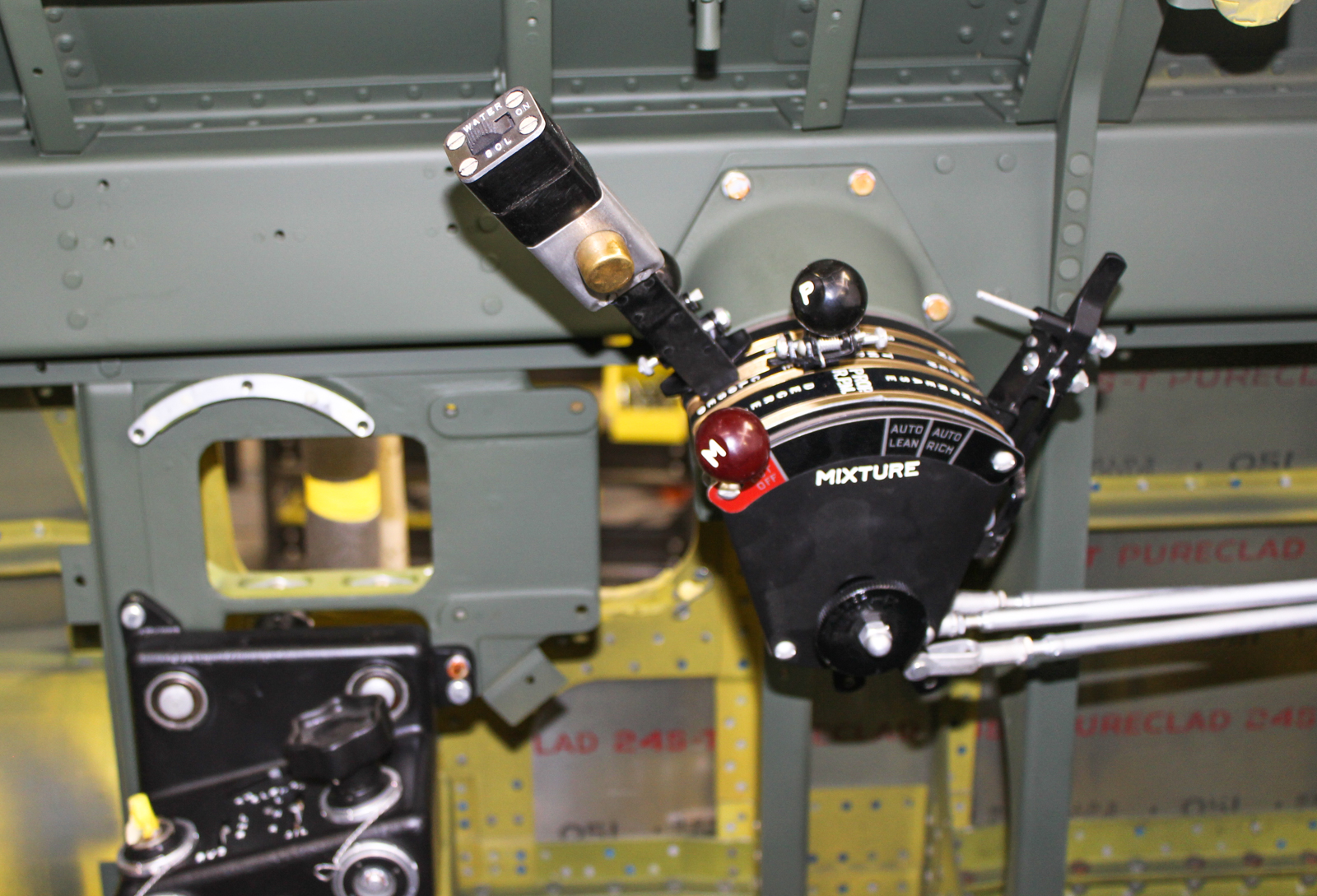
This month some custom paint mixing was done to accurately paint the cockpit interior. Engine control assemblies were also installed and some of the wing rib sections were fitted.
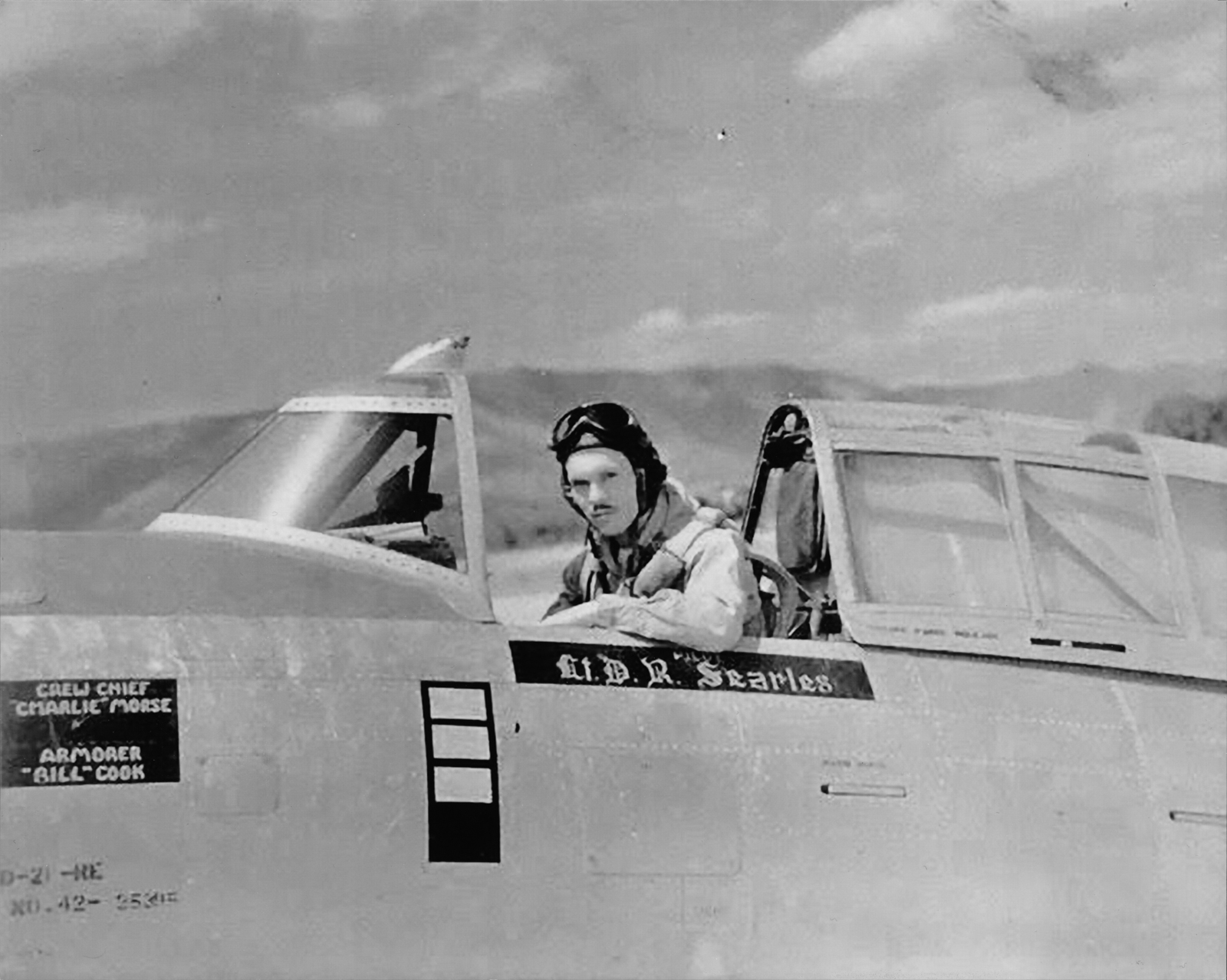
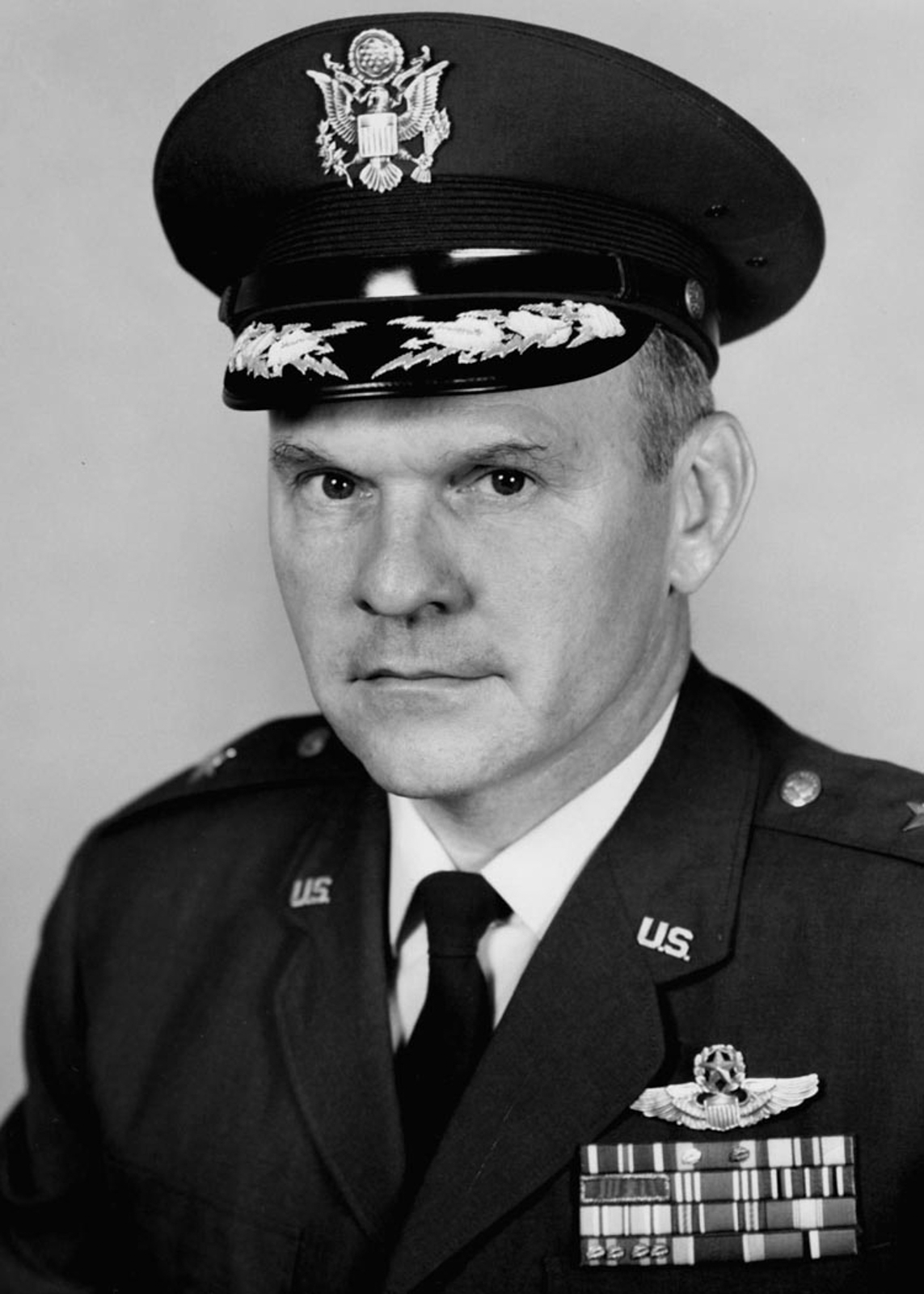
Major General Dewitt Searles, a Southwest Pacific Thunderbolt pilot, signed the main access door of the P-47. His career and accomplishments are highlighted in the history section of this update.
Cockpit Color
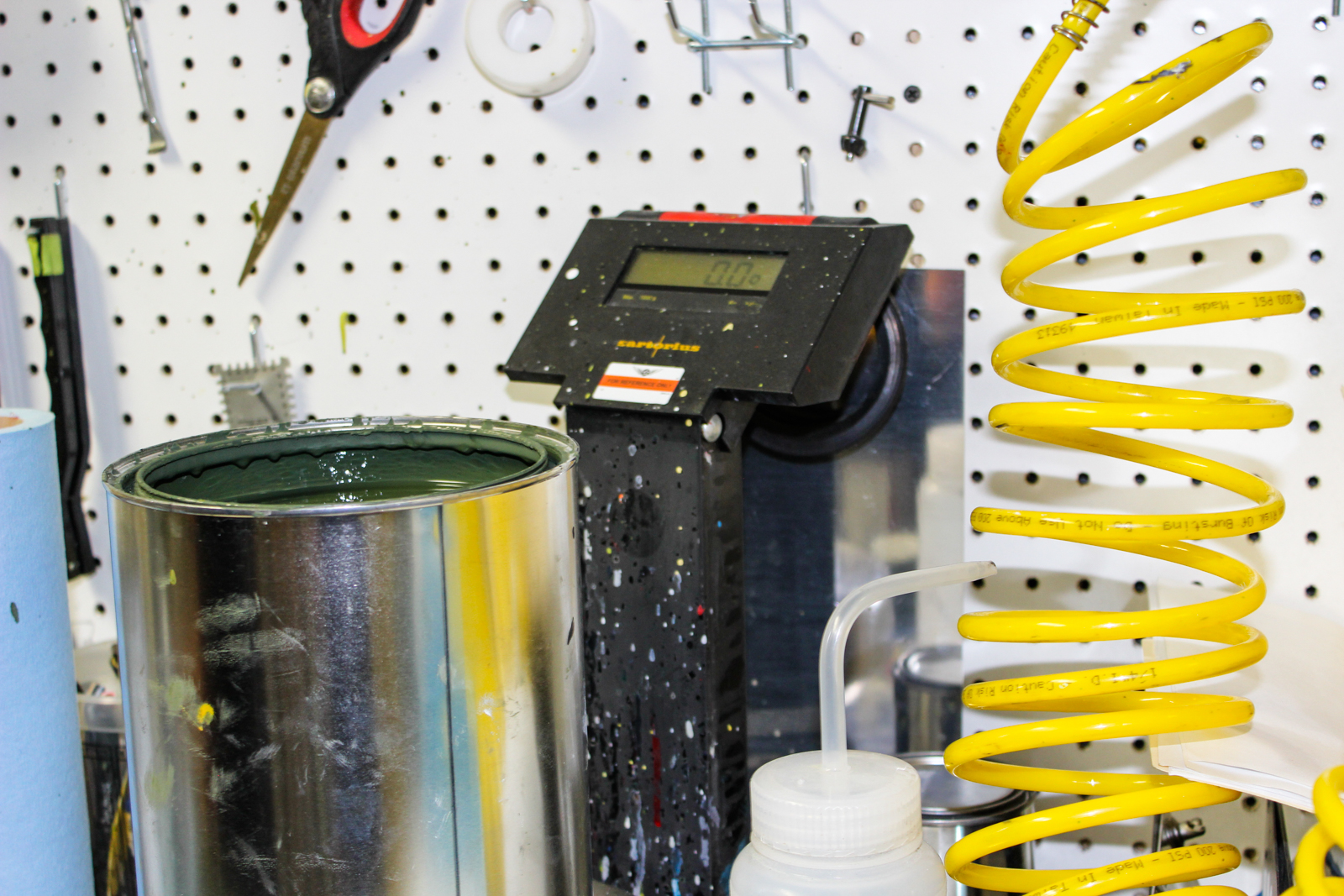
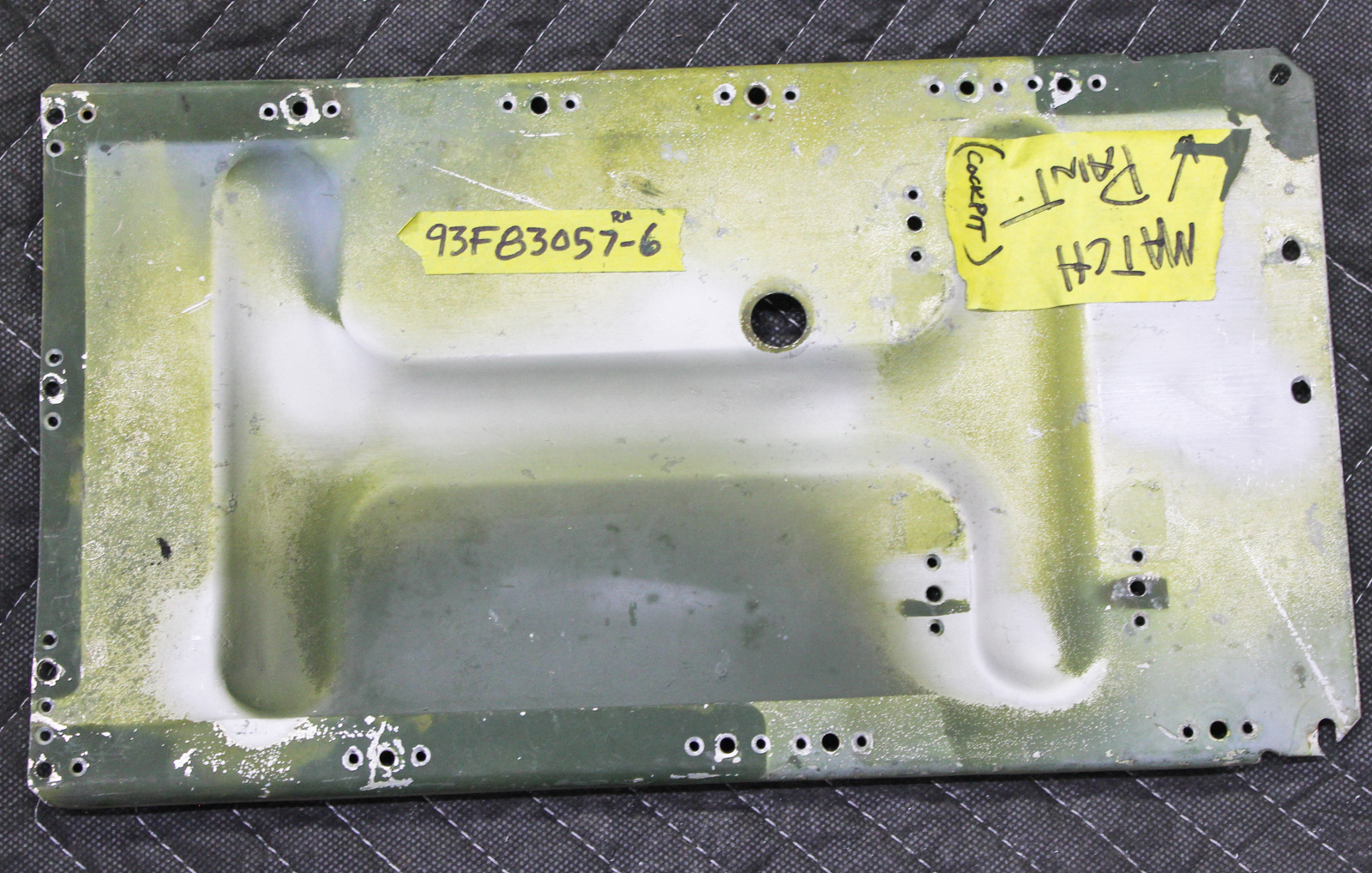
One of the challenges in an accurate restoration of a veteran warbird is getting the paint colors right for that specific airplane. Color standards are a start, but they aren’t the whole story. The inside of the cockpit on 42-27609 fortunately had a small area of undisturbed paint that had been covered by overlapping parts. It was fortunate because that paint didn’t precisely match the color specification called out in the engineering drawings.
The undisturbed paint is on part number 93F83057-6. It is the lower right front cockpit wall, original to our airframe, 42-27609. The panel’s importance lies in the paint along the edges.
Along those edges is paint that was covered by overlapping aluminum for 73 years. That green paint held its correct color because it wasn’t exposed to sunlight or weathering.
The 1944 color code specified for the cockpit is ANA 612 Shade #42 (Medium green), or in modern nomenclature, 34092. However, the original color in the sheltered area looked a little more brown than the specified 34092, and ended up being a closer match to 34079 on the Federal Standard 595C chart.
There are many possible reasons why the paint in the Thunderbolt doesn’t exactly match the color specified in the engineering drawings, but the most likely one relates to how rapidly P-47s were being produced at Evansville (and Farmingdale) at the time. With hundreds of P-47s rolling out of the factory, niceties like careful and complete shaking of paint likely went by the wayside, so paint from different levels in the original bulk container would dry to a slightly different shade after application.
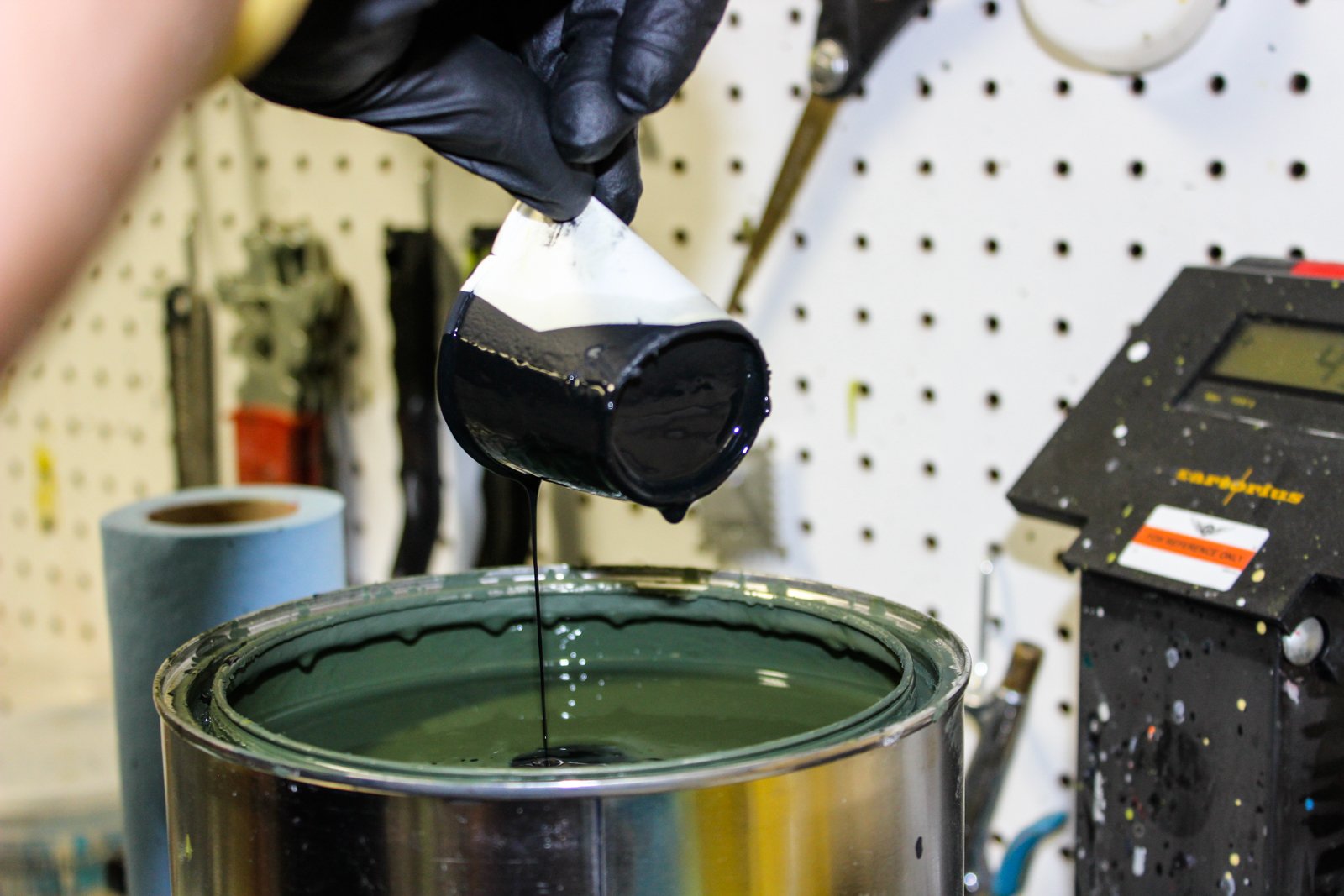
Dave Moyer, our talented painter, mixed paint to precisely duplicate the color.
Dave’s process involved adding a color, shaking the paint, shooting a small sample panel, and checking the results.
As the process continued, each time there was an addition of color, the paint was shaken to blend it and then the next color was added. This made for a long process, but it ensured that the final color was correct.
This procedure was repeated until Dave was satisfied that he had a perfect match for the original preserved color before he used the resulting paint to paint the interior of the cockpit of the Thunderbolt.
The following photos show the color. Note that different lighting angles and intensity make the color appear different in the various photos but the dark green is all the same custom mix to duplicate the original paint from 42-27609.
Cockpit
Once the paint was dry in the cockpit, control assemblies and other systems could be installed.
The members of the 35th Fighter Group weren’t fond of the water injection switch arrangement in their new D-23s, so they did a field modification; documented here.
The new P-47D-23s originally came with a water injection control that was a momentary switch that “must be depressed during the entire period in which water injection is employed.”
The 35th group didn’t like that arrangement because with one hand on the stick, and the other on the throttle to hold down the water injection switch button, “it is virtually impossible to trim the airplane for the increase in power obtained”.
Republic issued Tech order 01-65BC-114 to remedy the water injection control issue on subsequent P-47s. For utility reasons, the updated flashlight-type switch specified in the Tech Order is what will be used on 42-27609.
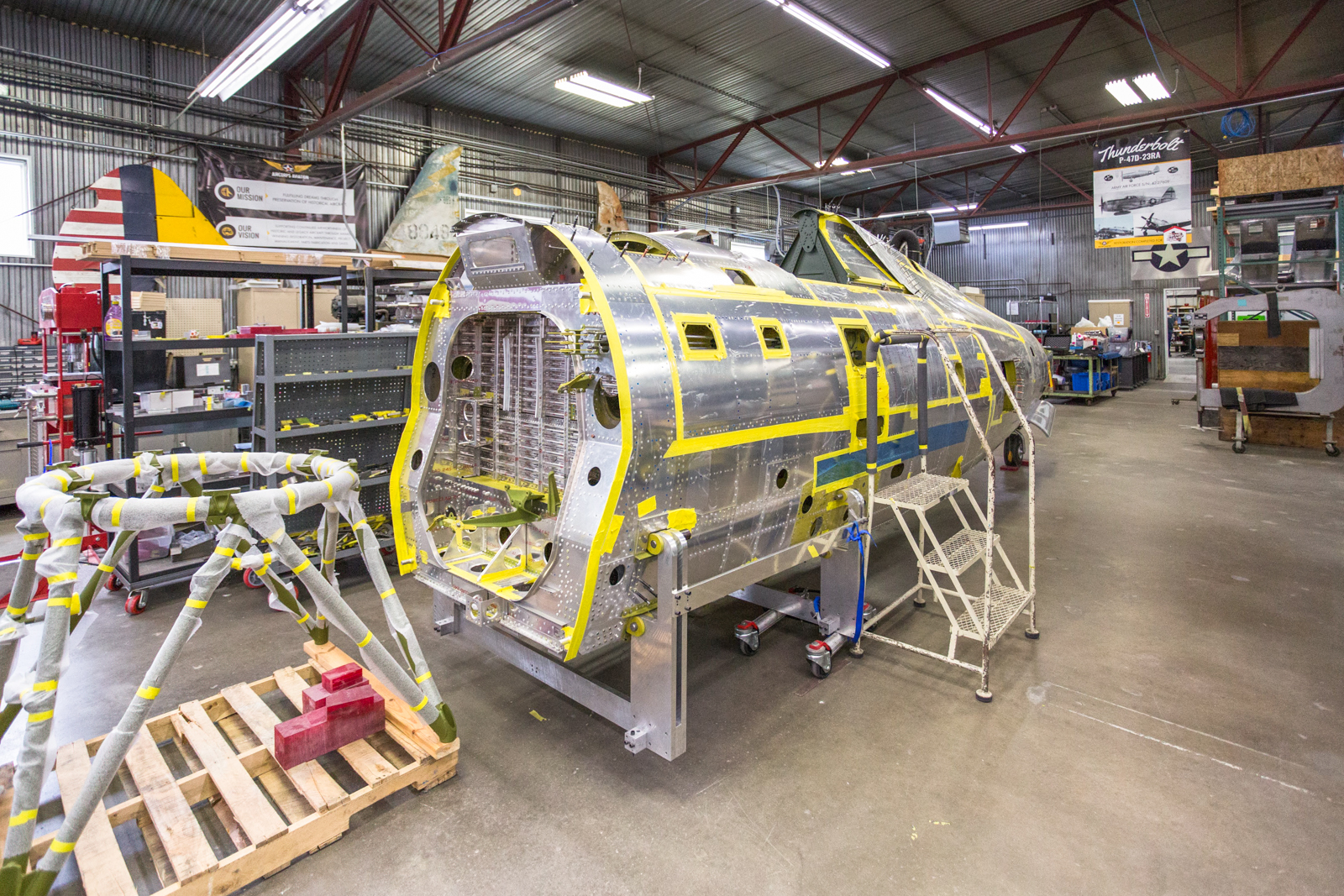
Fuselage Systems
Wings
More visible progress on the wing assembly happened this month than in recent months, as some of the rib sections were fitted.
An original rib is in place to verify if the rivet holes line up (it will be removed later). The angles on each side of the spar, and the part running from the top to bottom along the base of the spar, called the “ fitting assembly rib 26 ¾ and spar” ; are original parts that were extensively examined, tested and found to be airworthy.
Major General Dewitt Searles
It has been a great honor to correspond with Major General Dewitt Searles during our restoration of 42-27609.
Many thanks to Terry Popravak, author (with James Curran) of the fine book Check Six, a Thunderbolt Pilot’s War Across the Pacific [Jim Curran and Terrence Popravak Check Six!: A Thunderbolt Pilot’s War Across the Pacific ( Havertown, PA, Casemate Publishers, 2015)], for facilitating this connection. Major General Searles very recently celebrated his 99th birthday.
Here is what Maj. Gen. Searles had to say about the P-47 in an email to me:
“The P-47 was the sturdiest and most stable propeller driven aircraft that I have ever flown. It had an almost unlimited diving speed. I don’t recall a single incident of one breaking up in flight because of aerodynamic stress. And it could absorb more hits by enemy fighters or ground fire, and keep flying, than any other fighter plane that I know of.”
Biographical Information:
Dewitt Richard Searles was born on August 7, 1920 in Birmingham, Alabama, to Dewitt Richard and Miriam (Hostetler) Searles. His father died when Dewitt was 2 years old. Miriam Searles raised her son as a single mother in addition to contending with the significant challenges of the great depression.
Dewitt attended elementary and high school in Birmingham until his mother found a job as the school nurse at the Bolles School in Jacksonville Florida. After graduation from the Bolles School in 1939, he attended the College of William and Mary until 1941.
In the depression years, money for college was a real problem, especially for a single parent family. After two years at William and Mary, Dewitt enlisted in the aviation cadet program, and completed Army Air Force flying school training in 1943 with a commission as a second lieutenant, and his pilot wings.
During World War II, Lt. Searles served with the Far East Air Forces in the Pacific Theater of Operations.
Lt. Searles was assigned to the 348th Fighter Group, 342nd Squadron. Later he was assigned to the newly formed 460th Fighter Squadron, also part of the 348th Fighter Group. During World War II, Dewitt flew 269 combat missions against the Japanese. He is credited with shooting down three Japanese planes and, completed a total of 680 combat hours in P-47 Thunderbolts and P-51 Mustangs over New Guinea and the Philippines.
Major General Searles was kind enough to send me written summary of his war experiences which I will reproduce below in his words:
“A BRIEF SUMMARY OF THE WORLD WAR II EXPERIENCES OF DEWITT R. SEARLES, A FIGHTER PILOT, IN THE UNITED STATES ARMY AIR CORPS DURING THE 1943-45 TIME PERIOD.”
ln February 1941, with flying school completed, I began an accelerated training course in the combat aircraft I would fly when assigned to a unit overseas. lt was my great good fortune to be sent to Dale Mabry Army Airfield, Tallahassee, Florida, to begin training in the Republic P-47 Thunderbolt. Nicknamed the “Jug,” the P-47 was the biggest, most powerful and arguably the best multi-purpose fighter aircraft employed in World War ll. After completing transition training in July we traveled by train to Hamilton Field, Califomia for further deployment to the Southwest Pacific Area, and assignment to the recently formed 348th Fighter Group commanded by Col. Neel E. Kearby, soon to become a leading fighter ace and recipient of the Congressional Medal of Honor.
I was assigned to the Group’s 342nd Fighter Squadron and flown across the Pacific in the bomb bay of a modified B-24 bomber. We departed San Francisco and touched down at Hawaii, Canton Island, and on into the air base at Townsville, Australia where our aircraft awaited us – in crates. So our first mission was to uncrate the aircraft, put them together, test fly them, and then head across the Coral Sea to an air strip 5 miles from Port Moresby, New Guinea.
There we lived in canvas communities with tents on the bare ground for just about everything: sleeping, eating, supplies, maintenance and operations, flight line alert shack, field hospital, recreation, and even privies. Purified drinking water was delivered in water trailers and dispensed from huge canvas “lister” bags suspended from six-foot high tripods.
Our two greatest and most lethal challenges during my 22 month tour in New Guinea and the Philippines were the weather and mosquitoes. We lost more to them than we did to the Japanese. Just about every fighter pilot who flew in that area had a bad weather story to tell. The reason is that we had received little or no instrument flying training in any aircraft before being shipped overseas. “Needle, ball and airspeed” was about it, and that wouldn’t hack it in an area famous for massive, towering cumulus clouds and torrential rains. The worst weather experience for the Fifth Air Force – and perhaps the worst in aviation history – was on 16 April 1944: “Black Sunday.” On that one day we lost 37 aircraft to weather or weather related causes including: A-20’s. B-25’s, P-38’s, B-24’s, plus a P-39, a P-47, one F-5A, and one F-7A. To my knowledge there has never been a comparable one-day, noncombat, military aviation loss.
As for mosquitoes, they were our constant companions. They brought us Malaria and Dengue Fever. We fought them with Atabrine, DDT and mosquito nets. Daily Atabrine tablets turned the skin and the whites of the eyes yellow. DDT was the most effective and widely used killer/repellent but it came with harmful side effects, and mosquito nets were essential for a good night’s sleep. Used religiously, all three kept most of us fever free but mosquitoes got to enough of us to keep the hospital tent busy. DDT was banned for use in the United States, and in the military, in 1972, but it kept a lot of us going some 4O years ago in New Guinea’.
Food was the third thing that we found a little discouraging: powdered things like milk and eggs; canned things like C-rations and spam; dehydrated things like lemonade and coffee; and experimental things like tropical butter that wouldn’t spread or melt and that stuck to the roof of your mouth. And the lack of things like fresh fruit and vegetables added to our dietary problems. All of which points toward the thing we enjoyed most: combat flying.
The Jug was a devastating combat machine: eight .50 calibre machine guns, a 2000 horsepower supercharged engine with a four bladed prop; an unmatched high altitude capability that enabled us to gain speed while diving down into a fight instead of losing speed climbing up into one. We flew with confidence that if we used our heads we could survive just about anything that the Japs had to offer. And, surprisingly, was also the best fighter bomber in either theater of the war. We could easily handle a 100O pound bomb load. A favorite configuration was two 500 pound bombs, belly tank, and a full load of .50 calibre ammo. Jettison the tank, bomb the target and then follow up with a strafing attack more deadly than any other fighter plane could deliver.
The role of the P-47 steadily evolved as we moved up the northeastern coast of New Guinea and into the Philippines. lt changed from being an all purpose air-to-air/air to ground/combat patrol weapon to, primarily, a ground attack machine. Bombing and strafing became our principle mission. Either the Japanese were running out of aircraft or they began pulling them out of the theater for defense against an anticipated attack on the homeland by our combined military forces. ln any event, air-to-air engagements declined sharply. Toward the end, we concentrated almost exclusively on air to ground attacks, in support with our ground forces, with bombs, napalm, and machine gun fire. As an illustrative statistic: ln May 1945, the 460th Fighter squadron dropped more than 2000 tons of bombs, a record for bomb tonnage dropped by any fighter squadron in the war.
All the while we were moving rapidly up the northeast coast of New Guinea toward Douglas MacArthur’s initial objective, the Philippines. He meant it when he said: “l shall return!” He did. And he did it with an economy of force unmatched by any U.S. General since Winfield Scott in the 1846-48 War with Mexico.
From Brisbane, Australia he moved us across the Coral Sea to Port Moresby and then some 300 miles up the northeastern coast of New Guinea; leapfrogging from one air strip to the next: Moresby, Finschafen, Saidor, Wadke lsland, Biak, and Noemfoor. ln doing so, he left nearly a quarter million stranded and starving Japanese troops in his wake. Never once were the Japanese able to force him into a murderous man-to-man battle in the jungle. Those battles came after October 20, 1944 when MacArthur waded ashore at Leyte lsland and established a foothold in the Philippines. Twenty one days later we landed the first contingent of P-47’s on Leyte’s short, unfinished Tacloban air strip. The engineers were still laying pierced steel planking to extend the runway. Another 1000 feet had to be laid before it was fully operational. We arrived at Tacloban on the east side of Leyte at the same time that a Japanese naval task force sailed into Ormoc Bay on the west side of the island. The Japanese convoy composed of fully loaded troop ships, protected by destroyers, was
intended to reinforce troops in place and then to drive us off the island. The effort failed. We attacked the convoy the same day, along with a squadron of B-25’s from the 38th Bomb Group, and continued the attacks for several days afterwards. All the troop ships were sunk or ran aground and few, if any, of the men on board reached the fighting front.
We continued to move northward in support of the fight to drive the Japanese from the Philippines. On December 14th we moved to Tanauan air strip on Leyte and in February, 1945 we occupied San Marcelina air strlp, our first base on the main island of Luzon.
January 1945 was a particularly important month for me, personally, when, as a 24 year old 1st Lieutenant, l was given command of the 460th Fighter Squadron, a 300 man fighting unit equipped with 24 of the finest fighter aircraft ever built. Shortly afterwards I was promoted to Captain.
March 1945 also stands out in our history as we began transition from the gallant old “Jug” to the North American P-51 “Mustang.” To this day the arguments continue as to which was the better aircraft. Both were superb but my heart remains with the P-47.
May 1945 saw us move into the airstrip at Floridablanca, still further north, which enabled us to strike off-island targets as far away as Taiwan, as well as continuing our attacks on remaining targets on Luzon.
May was also my last month of combat duty in World War ll. On 3 May 1945, I received orders assigning me to the 24th Class at the Army Command and General Staff School, Fort Leavenworth, Kansas. While on leave, after completing the course at Leavenworth, two nuclear explosions brought the war to a close.
I’m reminded now of remarks made by Paul Tibbets a few years after the war when he was asked about the significance of the 509th Composite Group: the group of B-29 þombers which he commanded. Paul never used many words when a few would do. Here is what he said:
‘On August 6th we dropped our first atomic bomb. Three days later we dropped our second.’ Two days later Japan asked for peace, and three days later she got it. ‘That was the significance of the 509th Composite Group.’ “ [Dewitt Searles, “A BRIEF SUMMARY OF THE WORLD WAR II EXPERIENCES OF DEWITT R. SEARLES, A FIGHTER PILOT, IN THE UNITED STATES ARMY AIR CORPS DURING THE 1943-45 TIME PERIOD, via personal correspondence]
Major General Searles had a long and illustrious Air Force career after World War II, some highlights are listed below:
- Commissioned Second Lieutenant, United States Army Air Force, 1942
- Fighter pilot and squadron commander, New Guinea and the Philippines, 1943-1945
- Wing commander, 81st Tactical Fighter Wing, England, 1965-1967
- Inspector general, Tactical Air Command, Langley Air Force Base, Virginia, 1967-1969
- Commander, advanced through grades to major general, United States Air Force, 1971: 327th Air Division, Taiwan, Republic of China, 1969-1971
- Deputy commander, 7/13 Air Force, Udorn Air Force Base, Thailand, 1971-1972
- Deputy inspector general, Headquarters United States Air Force, Washington, 1972-1974, retired
- Assistant vice president, Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith, Washington, 1974-1987
- Retired, Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith, Washington, 1987
This month, we sent the main access door of the P-47 to Major General Searles for his signature.
and AirCorps Aviation are very thankful to Major General Searles for his generous cooperation in signing the access door. (photo via AirCorps Aviation)
And that’s all for this month. We wish to thank AirCorps Aviation, Chuck Cravens (words and images) as well as John LaTourelle and Aaron Prince (images) for making this report possible! We look forwards to bringing more restoration reports on progress with this rare machine in the coming months.