On this day in aviation history, 73 years ago (December 4, 1952), the Grumman S-2 Tracker flew for the first time. The S-2, known as the S2F, prior to 1962, was a twin-engined anti-submarine warfare (ASW) aircraft. The Tracker holds the distinction of being the first purpose-built aircraft for such a mission for the United States Navy. A conventional design, the S-2 features twin-radial engines, a foldable wing, and tricycle-retractable landing gear. In addition to serving with the United States Navy, the Tracker was produced for export to various nations – including Canada, Argentina, and Australia.
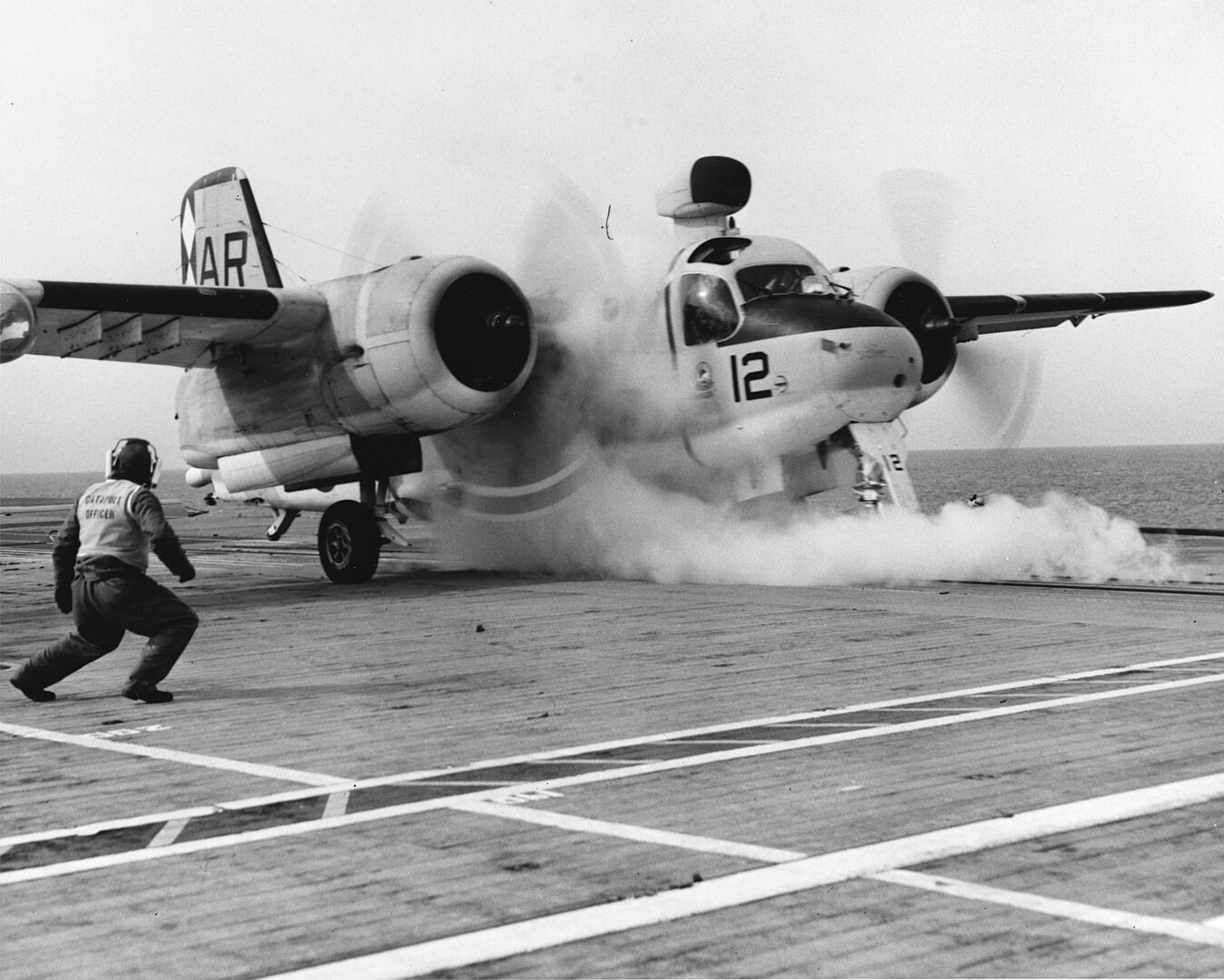

The Grumman S-2F model had a crew of four. Two 1,525-horsepower Wright R-1820-82WA 9-cylinder radial engines powered the Tracker to a cruise speed of 150 mph, though a maximum airspeed of 280 mph was attainable. The S-2 had a range of 1,173 nautical miles and a service ceiling of 22,000 feet. Armament came in the form of 4,800 pounds of munitions, which could be carried in the internal bomb bay and on six under-wing hardpoints. Mk. 34/41/43//44/46 torpedoes, Mk. 54 depth charges, or naval mines, could all be fitted as armament.
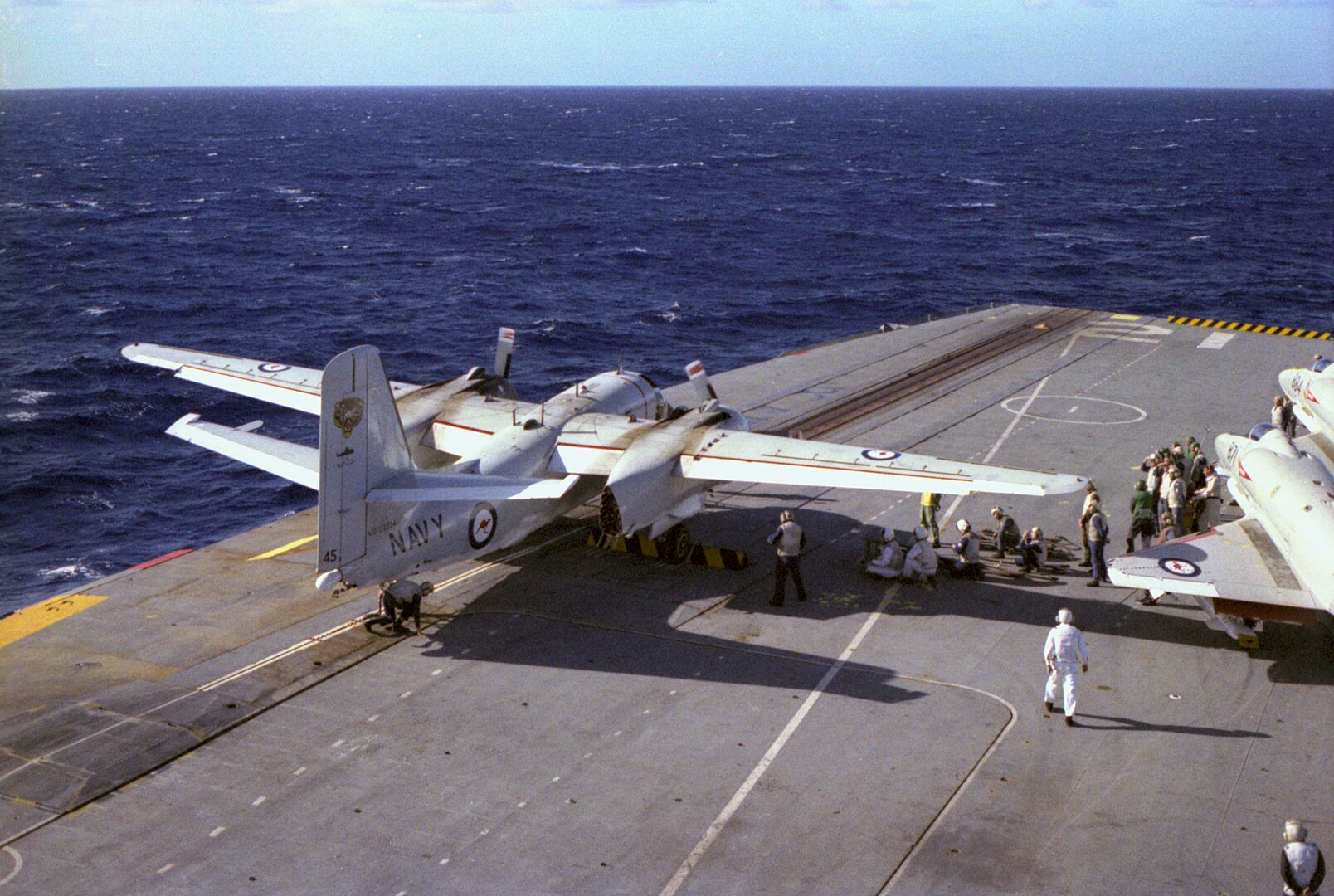

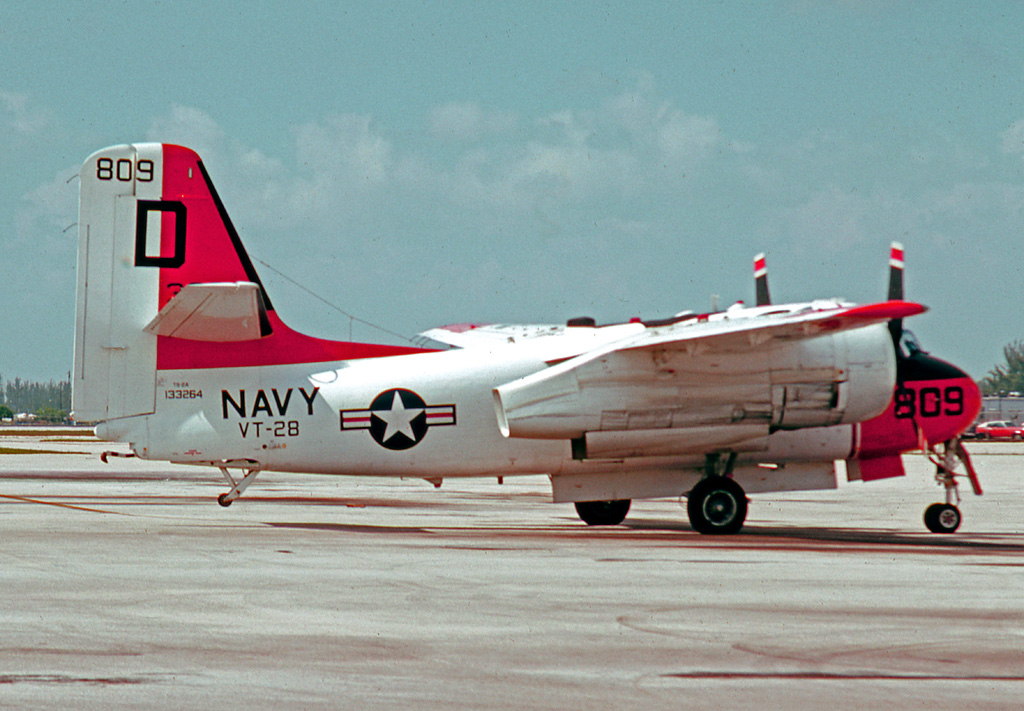
Grumman built a total of 1,284 Trackers during the aircraft’s production run. Two variants were also developed and manufactured, the C-1 Trader and E-1 Tracer. The C-1 Trader was a carrier-onboard delivery (COD) variant of S-2, built for hauling supplies between carriers and land bases. The E-1 Tracer was another airborne early warning variant, only with wings that folded backwards along the fuselage (instead of overhead, as on the C-1 and S-2).
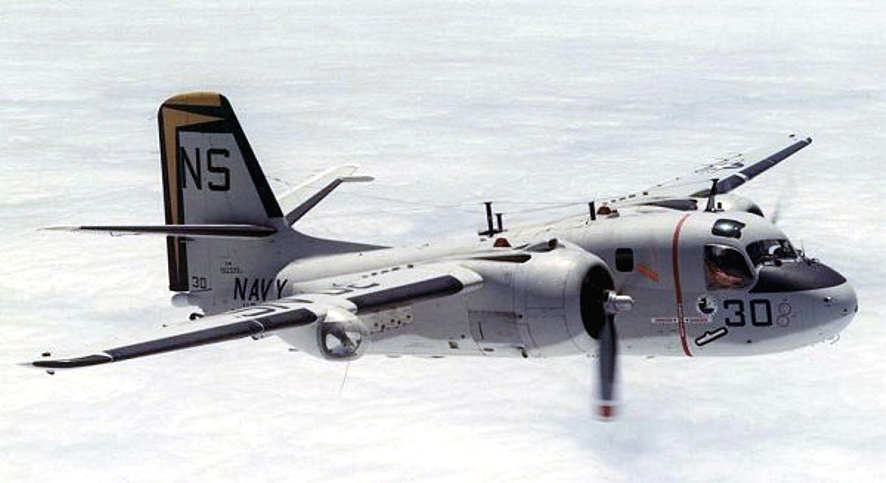

The Grumman S-2 has been retired from military service, but the aircraft had a long and successful career as an AEW ship. The last S-2s were retired from the Argentine Naval Aviation division on November 19, 2025 – just over a week ago (as of the writing of this article). The Canadian Warplane Heritage, in Hamilton, Ontario (Canada), is currently restoring a CS2F-2 Tracker to airworthy condition. Work on this aircraft, RCN 1577, has been slow but steady. Once complete, the CWH’s Tracker will help keep the Grumman S-2’s legacy alive for all to see and learn from.














![Catch-22 Star North American B-25 Mitchell Restoration Continues in Belgium 24 TB-25N 44-30925 in the Belgian Aircraft Preservation Association’s workshop at Gembloux. [Photo courtesy BAPA]](https://vintageaviationnews.com/wp-content/uploads/BAPA-B-25-20230312.jpg)








