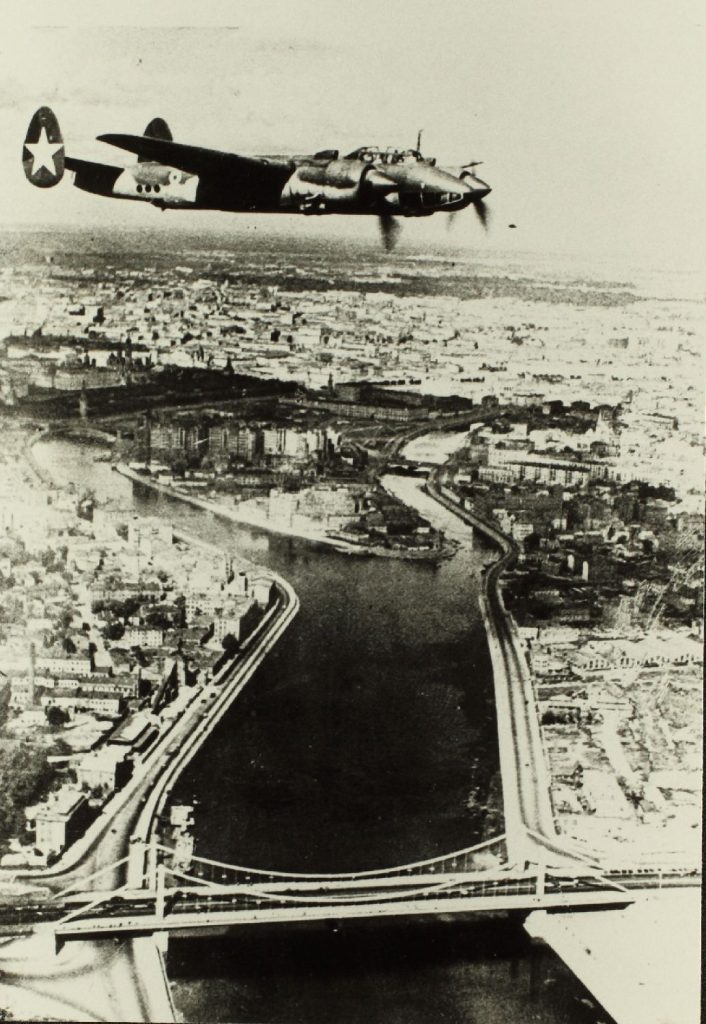
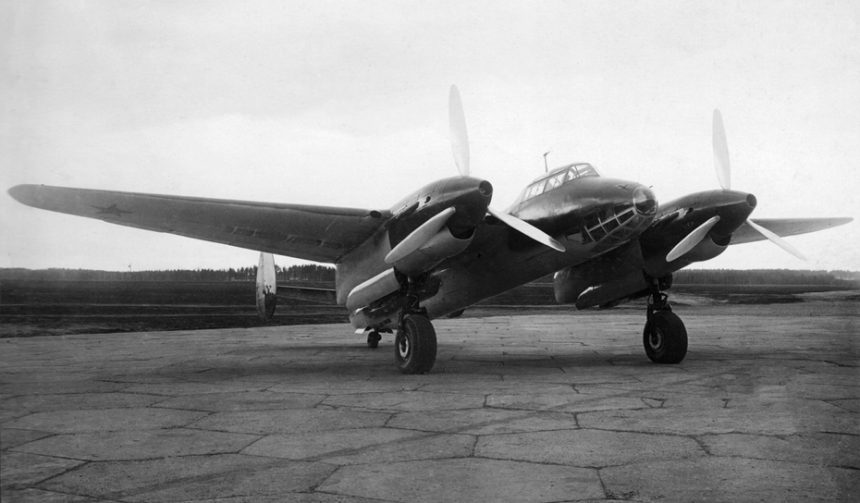
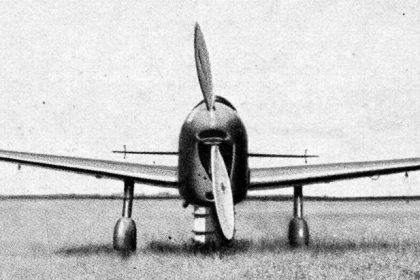
On this day in aviation history, 85 years ago (January 29, 1941), the Tupolev Tu-2 flew for the first time. Referred to as the Bat by NATO, the Tu-2 was a Soviet twin-engined high-speed frontline bomber used during World War II. Development of the Tu-2 began upon the issuance of a Soviet requirement for a high-speed bomber that could carry a large internal bomb load and fly as fast as a single-seat fighter of the period. Tupolev had the German Junkers Ju 88 in its sights when it designed the Tu-2, as during flight testing, it proved to be comparable.

Tupolev developed several variants of the Tu-2, much like Junkers had with the Ju 88. A torpedo, interceptor, and reconnaissance version of the aircraft was all produced. In combat, the Tu-2 proved to be effective and played a large role in the Soviet Red Army’s final offensives of the Second World War. During the Tu-2’s service, it was considered the second most important twin-engined bomber of the Soviet Air Force, only behind the Petlyakov Pe-2. Tu-2 pilots appreciated the aircraft’s fighter-like speed and maneuverability. Tupolev’s bomber began its service with the 132nd Bomber Aviation Regiment of the 3rd Air Army, and first saw combat at Velikiye Luki. Here, Tu-2s flew 46 sorties from November to December 1942.
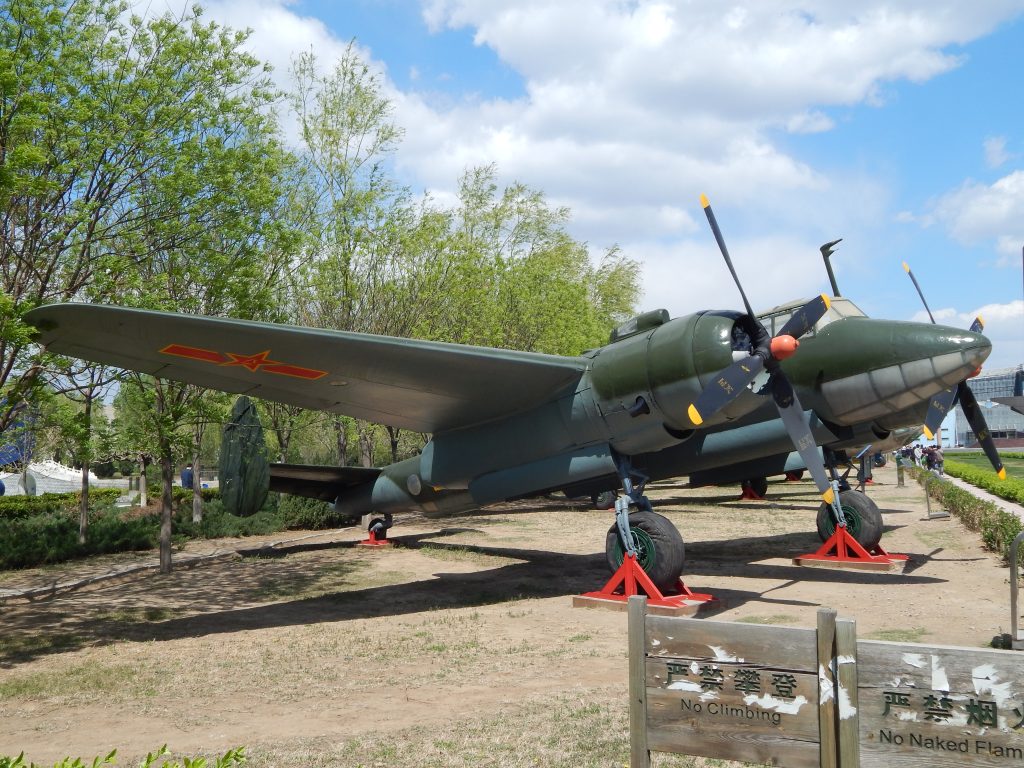

The Tupolev Tu-2 2M-82 had a crew of four and was powered by two 1,850-horsepower Shvetsov ASh-82 14-cylinder radial engines. The aircraft could attain a maximum airspeed of 328 mph and had a range of 1,090 nautical miles. The Tu-2’s service ceiling was 30,000 feet, with a 1,610-foot-per-minute rate of climb. The Tupolev was armed with two 20 millimeter ShVAK cannons in the wings, and three 7.62 millimeter rear-firing ShKAS machine guns in the canopy, dorsal and ventral hatches. These 7.62s were later replaced by 12.7 millimeter Berezin UB, and some Tu-2s were modified to have the Berezin B-20 cannon. Additionally, the Tu-2 could carry 3,300 pounds of bombs internally and 5,000 pounds externally.
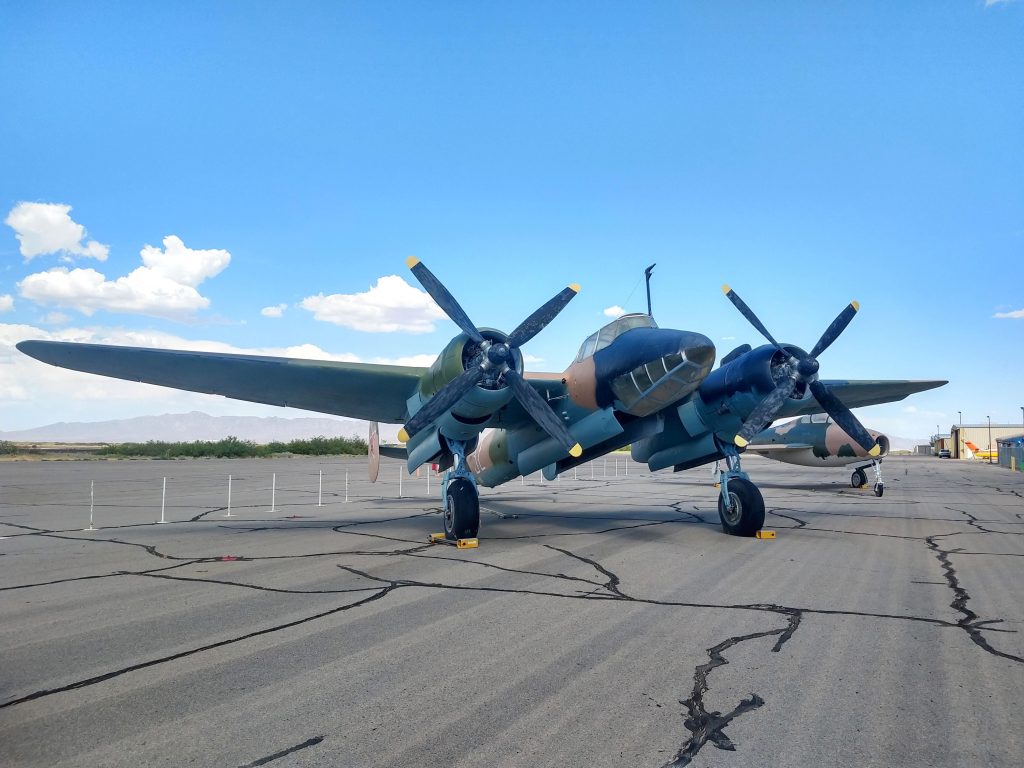

Tupolev built a total of 2,257 Tu-2s between 1941 and 1948. Eleven aircraft are known to survive today, many on display in China, Poland, and Russia. Two Tu-2s survive in the United States, one on static display at the War Eagles Air Museum in Santa Teresa, New Mexico. Kermit Weeks owns the other US-based Tu-2, which is currently in storage at the Fantasy of Flight Museum in Polk City, Florida.